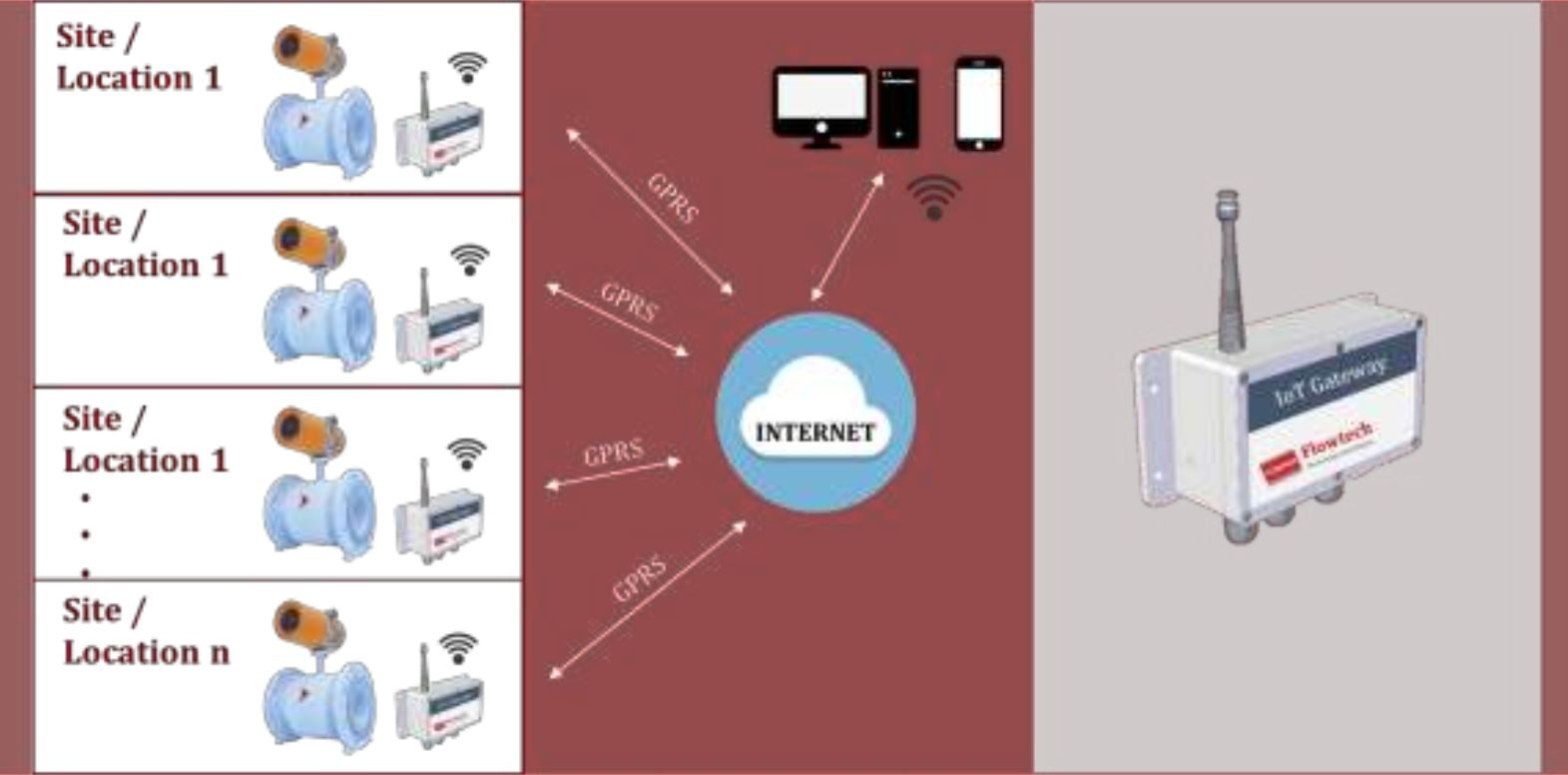
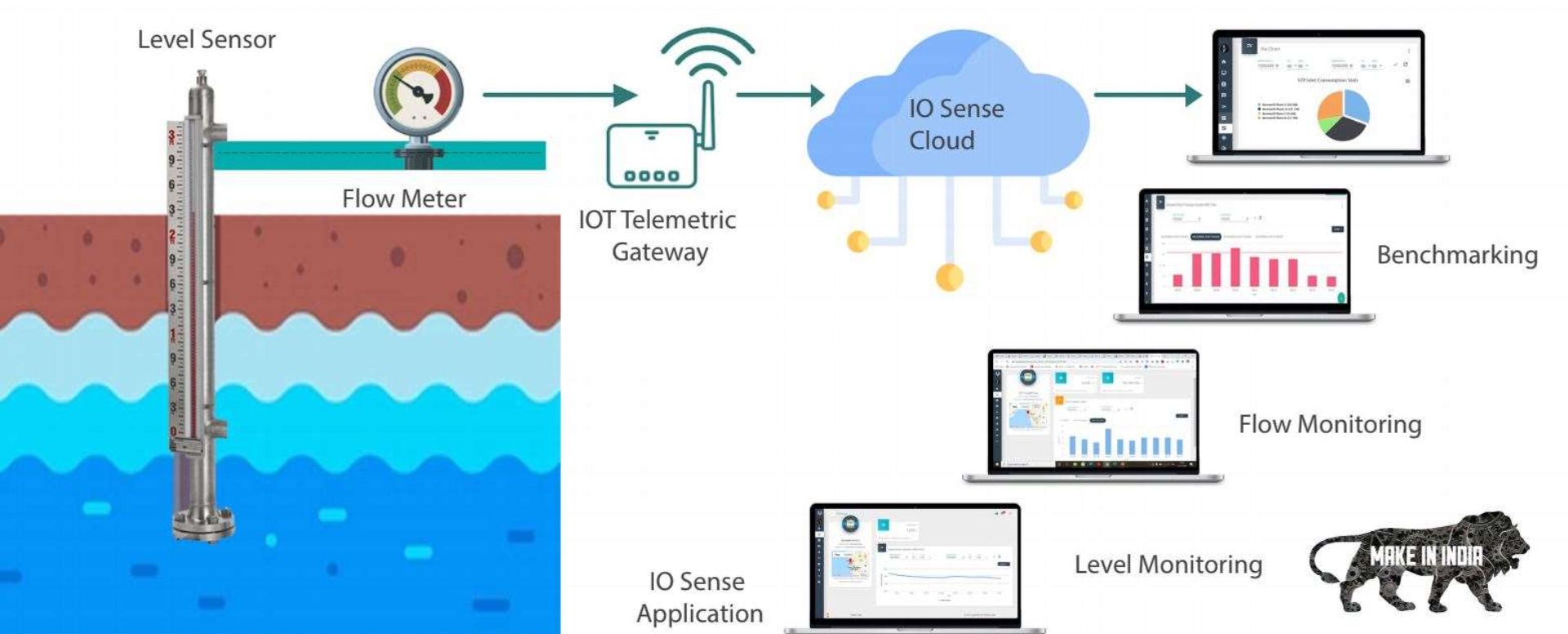
Introduction
Industrial flow measurement is no longer just about reading numbers on a meter. With the rise of AI, Big Data, and real-time monitoring, flow measurement has evolved into a smart, connected, and predictive technology. Today’s industries—from oil & gas to pharmaceuticals—demand not just accurate flow data, but also actionable insights that improve efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
This blog explores how AI-powered analytics, Big Data, and real-time monitoring are shaping the future of flow measurement—and what it means for industries worldwide.
Why Traditional Flow Measurement Isn’t Enough
Traditional flow meters (mechanical, turbine, or even older electronic models) provide basic flow readings, but they have limitations:
- Manual calibration and maintenance.
- Lack of integration with digital systems.
- Reactive troubleshooting (fixing problems only after failure).
- No predictive insights.
As industries move toward Industry 4.0 and digital transformation, these limitations slow down operations and increase costs.
AI in Flow Measurement
Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing flow measurement by enabling predictive and prescriptive intelligence.
Predictive Maintenance
AI models can analyze flow meter performance data and predict failures before they occur, reducing downtime and saving costs.
Anomaly Detection
AI detects abnormal patterns (like leaks, blockages, or pump inefficiencies) in real time, even before operators notice them.
Process Optimization
AI algorithms can continuously fine-tune processes based on flow patterns, improving efficiency and reducing waste.
Example: In oil refineries, AI-driven flow analysis can optimize crude oil blending by monitoring real-time flow rates and predicting quality outcomes.
Big Data in Flow Measurement
Flow meters today are data generators. With thousands of sensors installed across industries, the challenge is not measuring flow—but analyzing the vast amount of data.
Data Integration Across Plants
Big Data platforms collect flow data from multiple sites, enabling centralized control and benchmarking.
Advanced Analytics
By combining flow data with pressure, temperature, and energy consumption data, companies can unlock deeper insights into process efficiency.
Regulatory & Compliance Reporting
Automated data logging and cloud storage simplify reporting for ISO, NABL, and environmental compliance.
Example: A water treatment facility can use Big Data analytics to track flow variations across multiple stations, detect leaks instantly, and optimize pump energy usage.
Real-Time Monitoring and IIoT
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) makes real-time monitoring possible by connecting flow meters to digital networks.
Remote Monitoring
Operators can view flow rates, alarms, and diagnostics from anywhere, using web dashboards or mobile apps.
Instant Alerts
IoT-enabled flow meters can trigger alarms when abnormal conditions occur—like sudden drops in water pressure or gas leakage.
Digital Twins
Real-time flow data can be fed into a digital twin (a virtual model of a process), allowing simulation, forecasting, and “what-if” analysis.
Example: In smart cities, IoT-connected water meters enable real-time monitoring of distribution networks, preventing water losses and ensuring supply efficiency.
Benefits for Key Industries
Oil & Gas
- Real-time monitoring of pipelines prevents leaks and safety hazards.
- AI-powered analysis optimizes hydrocarbon flow and reduces energy costs.
Water & Wastewater
- Big Data ensures efficient water distribution and reduces non-revenue water losses.
- Predictive analytics detect leaks before they cause large-scale issues.
Food & Beverage
- Smart flow meters ensure compliance with hygiene and quality standards.
- Real-time monitoring supports precise batching and mixing.
Pharmaceuticals
- Ensures strict regulatory compliance through automated data logging.
- AI helps maintain consistency in critical liquid ingredients.
Challenges Ahead
While the future is promising, industries face hurdles in adopting AI and Big Data in flow measurement:
- High initial investment in smart meters and IIoT infrastructure.
- Data security and cybersecurity concerns.
- Need for skilled workforce to interpret AI and analytics outputs.
- Standardization of protocols for interoperability between devices.
What the Future Looks Like
- Self-Learning Flow Meters: Devices that adapt calibration automatically using AI.
- Edge Computing in Flow Meters: Processing data locally for faster insights without heavy reliance on cloud.
- Blockchain Integration: Ensuring secure and tamper-proof flow data for regulatory reporting.
- Sustainability Monitoring: Flow meters integrated with carbon footprint analysis to meet ESG goals.
Conclusion
The future of flow measurement lies in intelligent, connected, and predictive technologies. AI, Big Data, and real-time monitoring are not just trends—they are the foundation of Industry 4.0 flow management.
Organizations that embrace these technologies will enjoy:
✔️ Higher process efficiency
✔️ Reduced downtime
✔️ Stronger compliance
✔️ Greater sustainability
👉 At Flowtech Instruments, we’re committed to helping industries transition from traditional flow measurement to smart, future-ready solutions.
📩 Get in touch to explore how our advanced flow meters can power your digital transformation.